Microsoft SQL Server allows its
users to keep behavior of a database compatible to its older versions. Like, if
someone is using “*=” type of left outer joins in some quires/Stored Procedures
as she created it for SQL Server 2000. Though such join are not allowed in SQL
Server 2005 and subsequent versions but one still can keep database behavior as
SQL Server 2000 by keeping its compatibility level to 80.
Recently, a client reported that someone
(DBA or Application) is changing his database compatibility, which should
remain compatible to SQL Server 2000 (compatibility level 80). He wants to know
at what time this change is being made.
SQL Server 2008 and subsequent
versions keep record of this compatibility change to its log, but SQL Server
2005 has no such facility. It means, in SQL Server 2005, you never know when
someone has changed compatibility level.
In SQL Server 2008 and subsequent
versions one can change compatibility level of a database by following simple
TSql statement.
ALTER DATABASE
AdventureWorks SET COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL
= 90;
But in SQL Server 2005, only
method to change this compatability level is its system stored procedure i.e.
sys.sp_dbcmptlevel. SQL Profiler is the only place where you can trace when this
stored proecdure was executed. But what if, we need to place an alert for this
change and generate a mail for this change. Or what if, we need to stop
users/applications to change a database compatability level.
Only way to achieve this functionality
is, to update system stored procedure sp_dbcmptlevel.
Lets perform this task,
step by step.
Step 1: Stop SQL
Server 2005 services
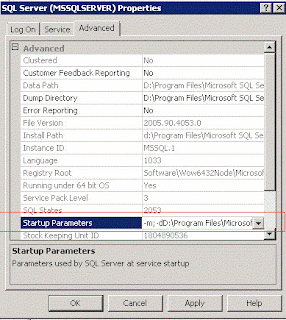
Step 2: Login using
DAC (Dadicated Administrative Connection). For this right click on SQL Server
2005 service, on Advanced tab, change startup parameters by adding -m; at
existing values.
Step 3: Start SQL Server 2005 services
Step 4: Open SQL Server Management Studio and open Database
Engine Query
Step 5: Login as valid sysadmin user or ADMIN:InstanceName
Step 6: Change mssqlsystemresource database to read_write mode
Step 7: It’s the time to update our system stored procedure
i.e. sp_dbcmptlevel.
If you need to keep only comptability level to
80 or 90 then change following lines of stored procedures with same values
i.e.80 or 90 or as per your choice.
select @cmptlvl60 =
60,
@cmptlvl60 = 65,
@cmptlvl60 = 70,
@cmptlvl60 = 80,
@cmptlvl60 = 90,
@cmptlvl60 = 65,
@cmptlvl60 = 70,
@cmptlvl60 = 80,
@cmptlvl60 = 90,
And if you also need to
add a mail alert for this change then add following code in error control
portion of stored procedure.
DECLARE @bodyText VARCHAR(200)
SET @bodyText='User '
+ CONVERT(VARCHAR,SYSTEM_USER)
+' trying to change Compatibility Level of Database ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR,@dbname)
+ ' at '
+ CAST(GETDATE() AS VARCHAR(50))
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail @recipients='essmess@gmail.com;', --Change Email Address Accordingly
@subject = 'Compatibility Level Change Alter',
@profile_name = 'DBTeam', --Change DB mail Profile Accordingly
@body = @bodyText,
@body_format = 'TEXT' ;
+ CONVERT(VARCHAR,SYSTEM_USER)
+' trying to change Compatibility Level of Database ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR,@dbname)
+ ' at '
+ CAST(GETDATE() AS VARCHAR(50))
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail @recipients='essmess@gmail.com;', --Change Email Address Accordingly
@subject = 'Compatibility Level Change Alter',
@profile_name = 'DBTeam', --Change DB mail Profile Accordingly
@body = @bodyText,
@body_format = 'TEXT' ;
Here is complete updated script
of stored procedure. (This script is only applicable to SQL Server 2005, for SQL Server 2008 and subsequent version, its totally different, which you can get by sp_helptext)
Step 8: Change mssqlsystemresource database to read_only mode
Step 9: Close SSMS
session, stop SQL Server services and change its startup parameters back to
normal.
Step 10: Start SQL Server
Services and you are done.












No comments:
Post a Comment
All suggestions are welcome